Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (35): 5710-5717.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1431
Previous Articles Next Articles
Meta-analysis of tripterygium glycosides combined with methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Yin Cong, Chen Xin, Sun Hui, Yu Axiang, Yuan Lijun, Tong Zhibin, Cheng Yinjie, Tu Xing
- (Department of Medicine, Hubei Minzu University, Enshi 445000, Hubei Province, China)
-
Received:2019-04-29Online:2019-12-18Published:2019-12-18 -
Contact:Tu Xing, MD, Master’s supervisor, Lecturer, Department of Medicine, Hubei Minzu University, Enshi 445000, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Yin Cong, Department of Medicine, Hubei Minzu University, Enshi 445000, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:the College Student Innovation and Entrepreneurship Program of Hubei Province, No. 201810517044 (to YC); the Key Project of Education Science Program of Hubei Province, No. 2016GA024 (to TX); the National Innovation and Entrepreneurship Program, No. 201810517006X (to YAX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yin Cong, Chen Xin, Sun Hui, Yu Axiang, Yuan Lijun, Tong Zhibin, Cheng Yinjie, Tu Xing. Meta-analysis of tripterygium glycosides combined with methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(35): 5710-5717.
share this article
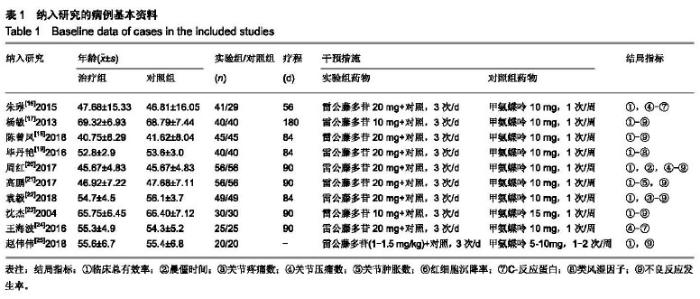
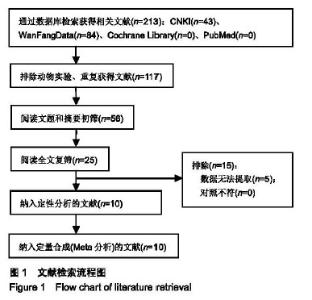
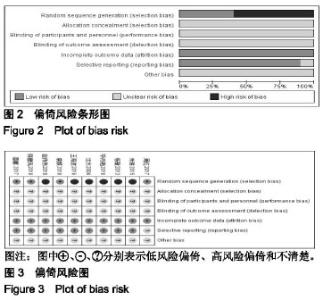
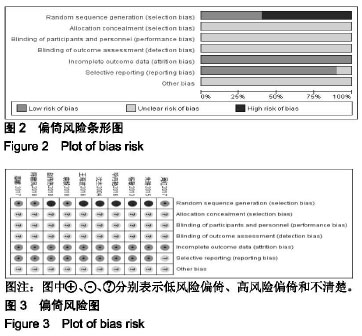
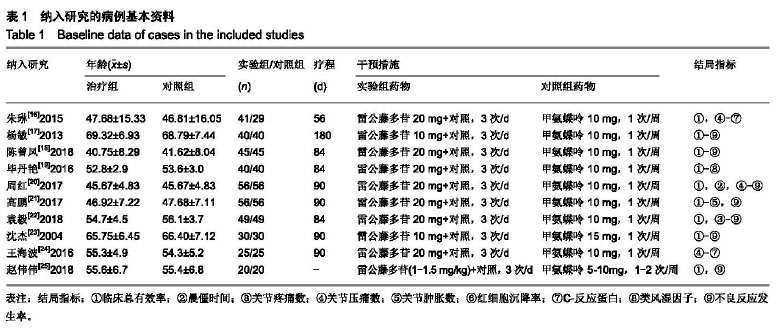
2.2 纳入文献的质量评价 采用Cochrane风险评价表评价其研究质量[26]。随机化方法:3篇采用随机数字表法[18,20-21],其余7篇提到了随机但未介绍具体的随机方法;分配隐藏:10篇均未提及;盲法:10篇均未提及;结果数据不完整:10篇均完整报道了研究结果;选择性报告:10篇均不清楚;所有文献均未说明是否存在其他偏倚。质量评价显示纳入的研究质量较低,图2,3。 2.3 疗效评价 2.3.1 临床总有效率 共有7个研究(n=462)报道了临床总有效率[17,18,20-23,25]。各研究间不存在统计学异质性(P=0.28, I2=20%),采用固定效应模型进行合并分析,结果显示,实验组临床总有效率显著高于对照组,差异有显著性意义[RR=1.23,95%CI(1.13,1.35),P < 0.000 01];提示雷公藤多苷联合甲氨蝶呤相较于单独使用甲氨蝶呤可更加有效提高类风湿性关节炎患者的临床总有效率,见图4。 "
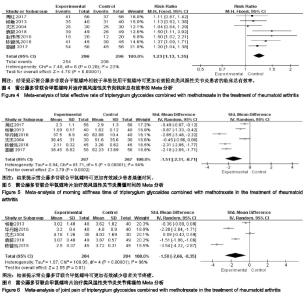
2.3.2 晨僵时间 共有6个研究(n=534)报道了晨僵时间的变化[17-21,23]。各研究间存在统计学异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=94%),采用随机效应模型进行合并分析,结果显示,实验组患者晨僵时间显著低于对照组,差异有显著性意义[SMD=−1.51,95%CI(-2.31,−0.71),P=0.000 2];提示雷公藤多苷联合甲氨蝶呤可更加有效减少患者晨僵时间,见图5。 2.3.3 关节疼痛 共有5个研究(n=408)报道了关节疼 痛[17-19,22,23]。各研究间存在统计学异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=96%),采用随机效应模型进行合并分析,结果显示,实验组患者关节疼痛显著少于对照组,差异有显著性意义[SMD=−1.50,95%CI(-2.66,−0.35),P=0.01];提示雷公藤多苷联合甲氨蝶呤可更加有效减少患者关节疼痛,见图6。 "
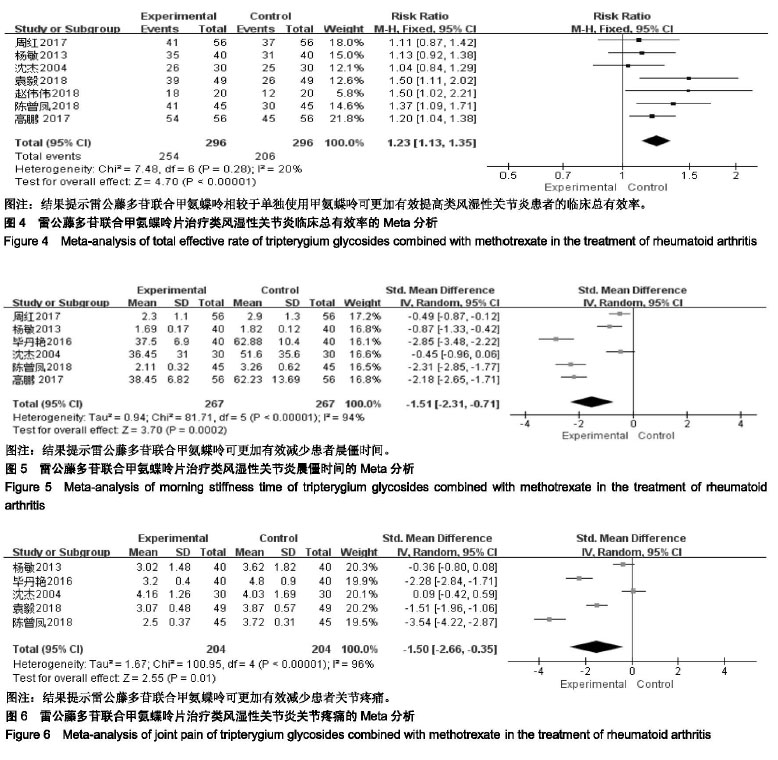
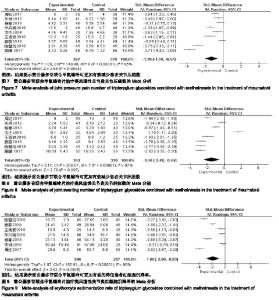
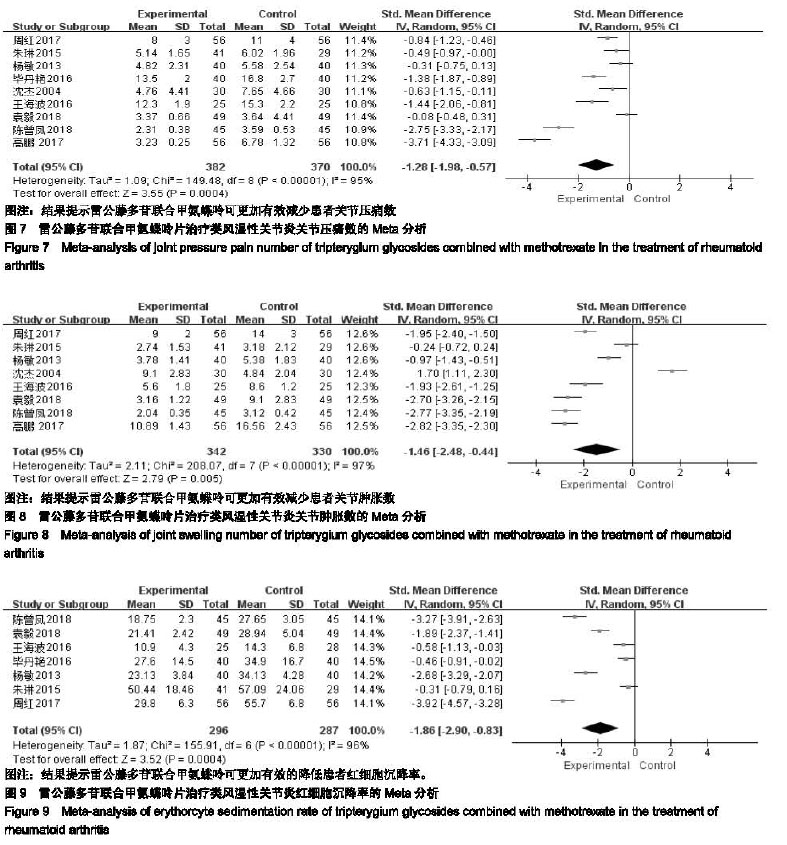
2.3.4 关节压痛数 共有9个研究(n=752)报道了关节压痛数[16-24]。各研究间存在统计学异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=95%),采用随机效应模型进行合并分析,结果显示,实验组患者关节压痛数显著少于对照组,差异有显著性意义[SMD=−1.28,95%CI(-1.98,−0.57),P=0.000 4];提示雷公藤多苷联合甲氨蝶呤可更加有效减少患者关节压痛数,见图7。 2.3.5 关节肿胀数 共有8个研究(n=672)报道了关节肿胀数[16-18,20-24]。各研究间存在统计学异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=97%),采用随机效应模型进行合并分析,结果显示,实验组患者关节肿胀数显著少于对照组,差异有显著性意义 [SMD=−1.46,95%CI(-2.48,−0.44),P=0.005];提示雷公藤多苷联合甲氨蝶呤可更加有效减少患者关节肿胀数,见图8。 2.3.6 红细胞沉降率 共有7个研究(n=583)报道了红细胞沉降率的变化[16-20,22,24]。各研究间存在统计学异质性 (P < 0.000 01,I2=96%),采用随机效应模型进行合并分析,结果显示,实验组患者红细胞沉降率显著低于对照组,差异有统计学意义[SMD=−1.86,95%CI(-2.90,−0.83),P=0.000 4];提示雷公藤多苷联合甲氨蝶呤可更加有效的降低患者红细胞沉降率,见图9。 "
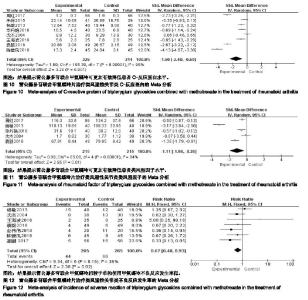
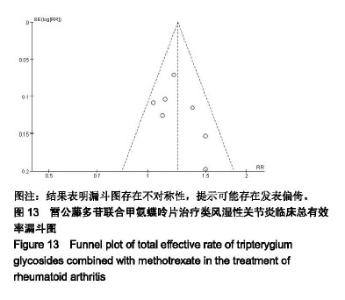
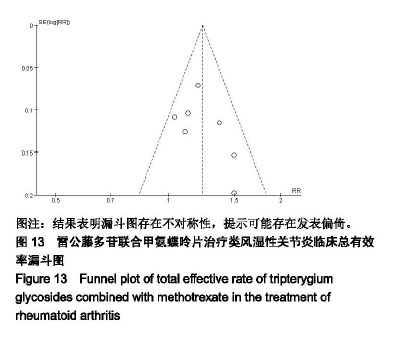
2.3.7 C-反应蛋白 共有8个研究(n=640)报道了C-反应蛋白的变化[16-20,22-24]。各研究间存在统计学异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=96%),采用随机效应模型进行合并分析,结果显示,实验组患者C-反应蛋白水平显著低于对照组,差异有显著性意义[SMD=−1.50,95%CI(-2.40,−0.60),P=0.001];提示雷公藤多苷联合甲氨蝶呤可更加有效降低患者C-反应蛋白水平,见图10。 2.3.8 类风湿因子 共有5个研究(n=430)报道了类风湿因子的变化[17,19,20,22-23]。各研究间存在统计学异质性(P < 0.000 01,I2=94%),采用随机效应模型进行合并分析,结果显示,实验组患者类风湿因子水平显著低于对照组,差异有显著性意义[SMD=−1.11,95%CI(-1.96,−0.26),P=0.01];提示雷公藤多苷联合甲氨蝶呤可更加有效降低患者类风湿因子水平,见图11。 2.3.9 不良反应发生率 共有7个研究(n=110)报道了不良反应发生率[17,18,20-24]。各研究间不存在统计学异质性(P=0.16,I2=36%),采用固定效应模型进行合并分析,结果显示,实验组患者不良反应发生率显著少于对照组,差异有显著性意义[RR=0.67,95%CI(0.48,0.93),P=0.02];提示雷公藤多苷联合甲氨蝶呤相较于单独使用甲氨蝶呤不良反应发生率低,见图12。 2.4 发表偏倚分析 应用Revman5.3对纳入文献通过绘制漏斗图进行偏倚风险评估。以临床总有效率为评价指标,以各研究效应量RR的对数值为纵坐标,以RR值为横坐标绘制倒漏斗图,结果表明漏斗图存在不对称性,提示可能存在发表偏倚,见图13。 "

| [1]Picerno V, Ferro F, AdinolfiA,etal.One year in review: the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. ClinExpRheumatol. 2015;33(4):551.[2]Gao Q, Wang YX, Xu D, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis: pathological mechanisms and modern pharmacologic therapies. Bone Res.2018;(6): 15.[3]池里群,周彬,高文远,等.治疗类风湿性关节炎常用药物的研究进展[J].中国中药杂志, 2014,39(15):2851-2858.[4]昊霞,林兵,王忠震,等.雷公藤的免疫抑制活性及毒性的谱效关系研究[J].中国医院药学杂志,2016,36(7):547-552.[5]黄晶,舒晓明,王贵,等.甲氨蝶呤治疗类风湿关节炎的作用机制[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2016,10(21):3276-3280.[6]杨冬梅,刘俊.雷公藤多苷临床应用及不良反应的研究进展[J].中国医院药学杂志,2018,38(20):2185-2190.[7]王娟芳.雷公藤治疗类风湿性关节炎的疗效观察[J].内蒙古中医药,2017,36(04):31.[8]Lv QW, Zhang W, Shi Q, et al. Comparison of Tripterygiumwilfordii Hook F with methotrexate in the treatment of active rheumatoid arthritis (TRIFRA) :a randomized, controlled clinical trial.Ann Rheum Dis.2015; 74(6):1078-1086.[9]吴琼.门急诊超适应证处方调查及其对策[J].中医药管理杂志, 2018,26(20):24-26.[10]张晓攀,李艳贞,李珊珊,等.类风湿性关节炎治疗药物研究进展[J].药物评价研究,2018,41(10):1906-1910.[11]Saag KG, Teng GG, Patkar NM, et al.American College of Rheumatology 2008 recommendations for the use of nonbiologic and biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum.2008; 59(6): 762-784.[12]Smolen JS, Lendewe R, Breedveld FC, et al.EULAR rec-ommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying anti-rheu-matic drugs.Ann Rheum Dis.2010;69(6):964-975.[13]郑筱萸.中药新药临床研究指导原则(试行)[S].北京:中国医药科技出版社,2002:115.[14]吕芳,李兴福.2010年美国风湿病学会联合欧洲抗风湿病联盟的类风湿关节炎分类标准解[J].诊断学理论与实践, 2010,9(4): 307-310.[15]郑明华.Meta分析软件应用与实例解析[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2013.[16]朱琳,陈鹏.甲氨蝶呤联合雷公藤多苷与单用甲氨蝶呤治疗类风湿关节炎效果比较[J].检验医学与临床, 2015,12(23): 3568-3570.[17]杨敏,周润华,李宝贞,等.甲氨蝶呤联合雷公藤多苷治疗老年类风湿关节炎[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2013,19(17):300-304.[18]陈曾凤,兰培敏,陈汉玉,等.雷公藤多苷联合甲氨蝶呤治疗类风湿关节炎活动期患者的疗效及对血清CD62p?CD41的影响[J].现代生物医学进展,2018,18(20):3909-3912+3921.[19]毕丹艳,李芹,张虹,等.雷公藤多苷联合甲氨蝶呤治疗类风湿关节炎的临床疗效研究[J].中国临床药理学杂志, 2016,32(10): 880-882.[20]周红.雷公藤多苷与甲氨蝶呤联合治疗类风湿关节炎的疗效分析[J].中国医药指南,2017,15(06):191.[21]高鹏,霍爱鑫,刘宇宏.雷公藤多苷联合甲氨蝶呤治疗类风湿性关节炎的疗效[J].西部医学,2017,29(11):1511-1515.[22]袁毅.雷公藤多苷联合甲氨蝶呤治疗类风湿关节炎效果观察[J].临床医学,2018,38(1):100-101.[23]沈杰.雷公藤多苷联合小剂量甲氨蝶呤治疗老年性类风湿关节炎临床观察//中国中西医结合学会皮肤性病专业委员会.第四次全国雷公藤学术会议论文汇编[C].中国中西医结合学会皮肤性病专业委员会:中国中西医结合学会,2004.[24]王海波,崔永虹,刘杰.雷公藤多苷片联合甲氨蝶呤片治疗类风湿性关节炎临床分析[J].临床合理用药杂志,2016,9(35):52-53.[25]赵伟伟.评价雷公藤多苷联合甲氨蝶呤治疗类风湿关节炎的疗效及安全性[J].首都食品与医药,2018,25(22):38.[26]尹聪,陈鑫,涂星,等.灯盏细辛注射液不良反应的Meta分析[J].中国民族民间医药,2018,27(15):47-54.[27]李淼,刘志丹,赵创,等.类风湿关节炎相关microRNA 研究进展[J].国际免疫学杂志,2017,40(4): 429-434.[28]Louthernoo W, Nilganuwong S, Nanagara R, et al. THU0207 Diacere in Combination with Methotrexate versus Methotrexate Alone in The Treatment of Early Rheumatoid Arthritis.2016;75(2):262.[29]Mirzaei A, Ataeipoor Y, Asgari M, et al. Seropositivity of Rheumatoid Arthritis Specific Tests in a Patient With Nephrotic Syndrome: Successful Treatment With Rituximab. Iran J Kidney Dis.2017;11(6):467-468.[30]Aota Y, Nonaka T, Kimura S, et al. A methotrexate-associated Lympholiferative disorder patient with gastrointestinal perforation.Nihon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi.2017; 54(4): 567-572[31]Papachristou M, Kastis GA, Stavrou PZ, et al. Radiolabeled methotrexate as a diagnostic agent of inflammatory target sites: A proof-of-concept study. Mol Med Rep.2018;17(2): 2442-2448.[32]杨敏,周润华,李宝贞,等.甲氨蝶呤联合雷公藤多苷治疗老年类风湿关节炎[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2013,19(17) : 300-304.[33]Li H, Guo F, Luo YC, et al. Efficacy of tripterygium glycosides tablet in treating ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Rheumatol.2015; 34(11): 1831-1838.[34]陈秀敏,黄闰月,晏菁遥,等.化瘀通痹方联合甲氨蝶呤治疗难治性类风湿关节炎临床观察[J].中国中西医结合杂志, 2015,35(11): 1326-1330. |
| [1] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [2] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [3] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [4] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [5] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [6] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [7] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [8] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [9] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [10] | Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976. |
| [11] | Zhan Fangbiao, Cheng Jun, Zou Xinsen, Long Jie, Xie Lizhong, Deng Qianrong. Intraoperative intravenous application of tranexamic acid reduces perioperative bleeding in multilevel posterior spinal surgery: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 977-984. |
| [12] | Liu Qing, Wan Bijiang. Effect of acupotomy therapy on the expression of Bcl-2/Bax in synovial tissue of collagen-induced arthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 729-734. |
| [13] | Zhong Yuanming, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng, Wu Zhuotan, He Bingkun, Wu Sixian. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty and unilateral pedicle approach percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 456-462. |
| [14] | Li Yang, Zhang Mingyong. Meta-analysis of the effect of double Endobutton and clavicular hook plate on the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 463-470. |
| [15] | Li Yanle, Yue Xiaohua, Wang Pei, Nie Weizhi, Zhang Junwei, Tan Yonghai, Jiang Hongjiang. Intramedullary nail fixation versus plate fixation in the treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 471-476. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||